เริ่มต้น Django RestFramework
- https://medium.com/@wasinthiengkunakrit/%E0%B8%81%E0%B8%B2%E0%B8%A3%E0%B9%83%E0%B8%8A%E0%B9%89%E0%B8%87%E0%B8%B2%E0%B8%99-django-restframework-94e08255fe3c

ปัจจุบันการพัฒนาเวปไซด์จะแยกการพัฒนาออกเป็น FrontEnd (เช่น React, Angular, Vue) และ BackEnd ( เช่น Django ) ซึ่งสิ่งที่ใช้เป็นสื่อกลางในการแลกเปลี่ยนข้อมูลกันระหว่าง FrontEnd และ BackEnd คือ Rest API นั่นเอง ในบทความนี้จะเป็นการอธิบายการสร้าง BackEnd ให้รองรับ Rest API ด้วย Django โดยได้มีการเลือกใช้ Library ชื่อ Django Rest framework เพื่อช่วยให้การพัฒนา REST API ทำได้อย่างง่ายดายและรวดเร็ว
สิ่งที่ต้องเตรียม
Python 3.7
ความรู้ด้านการเขียน Django ขั้นพื้นฐาน ( สร้าง model และเขียน view ได้ )
ติดตั้ง package พื้นฐานด้วยคำสั่งต่อไปนี้ $ pip install -r requirements.txt
ทำความรู้จักกับ REST API
REST API คือข้อกำหนดที่ใช้ในการแลกเปลี่ยนข้อมูลระหว่าง FrontEnd และ BackEnd โดยทั่วไปข้อกำหนดนี้จะถูกใช้งานอยู่บน HTTP Protocol
HTTP Protocol คือ message ที่ใช้รับและส่งกันระหว่าง web browser (FrontEnd) กับ Web Server (Backend/Django) ซึ่งลักษณะของ HTTP Request จะอยู่ในรูปแบบของ text message ที่สามารถแบ่งชิ้นส่วนออกมาได้ตามรูปต่อไปนี้

ส่วน Request Line ใช้สำหรับบอกว่า HTTP message นี้ใช้ทำอะไร ซึ่งส่วนสำคัญคือส่วนที่อยู่ด้านหน้าสุดของบรรทัดที่เรียกว่า HTTP Method ซึ่งจากรูปจะเป็น HTTP Method “POST” โดยข้อตกลง REST API จะแบ่ง HTTP Method ออกเป็น 1.1 GET หมายถึง HTTP Message นี้ต้องการดึงข้อมูลบางอย่างจาก server 1.2 POST หมายถึง HTTP Message นี้ต้องการสร้างข้อมูล (Create) ขึ้นมาใหม่บน server 1.3 PUT หมายถึง HTTP Message นี้ต้องการแก้ไข (Update)ข้อมูลบน server 1.4 PATCH หมายถึง HTTP Message นี้ต้องการแก้ไขข้อมูลบางส่วน (Partial Update) บน server 1.5 DELETE หมายถึง HTTP Message นี้ต้องการลบข้อมูลบน server
ส่วน HTTP Header เป็นส่วนที่ใช้ระบุรายละเอียดของ HTTP message นี้ เช่น ชนิดของ browser ที่ส่งข้อมูลมา, ระบุ Token สำหรับยืนยันตัวตนของผู้ใช้งาน, ชนิดข้อมูลของ Body มี format แบบไหน, ความยาวของ Body มีจำนวนกี่ตัวอักษร เป็นต้น
ส่วนของ HTTP Body เป็นข้อมูลที่รับและส่งกับ web server โดยปกติแล้ว REST API จะใช้มาตรฐาน JSON (Javascript Object Notation) ในการแลกเปลี่ยนข้อมูล
ดังน้ันโดยสรุปแล้วหน้าที่ของ Django ในการจัดการ REST API คือรอรับ HTTP Message จาก Browser (FrontEnd Client) แล้วตีความว่า client ต้องการทำอะไร กับข้อมูลที่เก็บอยู่ใน database แล้วสร้าง JSON message เพื่อตอบกลับ client ให้ถูกต้องนั่นเอง
เริ่มต้น Checkout Tutorial Project
เพื่อความรวดเร็วในบทเรียน จะอ้างอิง code ที่ checkout มาจาก
https://github.com/WasinTh/rest_tutorial
ซึ่ง project นี้เก็บข้อมูลของ Author และ Book และมี REST API เพื่อใช้จัดการกับข้อมูลของ Author และ Bookภาพตัวอย่างฐานข้อมูลที่ใช้ในการทดลองครั้งนี้

โครงสร้างไฟล์ของ project มีดังต่อไปนี้
db.sqlite3 คือไฟล์ database ที่เก็บข้อมูลของ Author และ Book
manage.py เป็นไฟล์สำหรับรัน Django project
rest_tutorial โฟลเดอร์ใช้สำหรับเก็บ urls.py และ settings.py ของ project
library โฟลเดอร์ application ที่จะใช้ในบทความนี้ 4.1 sample_1 เป็นตัวอย่าง code การสร้าง REST API โดยไม่ใช้ framework 4.2 sample_2 เป็นตัวอย่าง code การใช้งาน serializer ของ Django Rest framework 4.3 sample_3 เป็นตัวอย่าง code การใช้งาน Generics API View 4.4 sample_4 เป็นตัวอย่าง code การใช้งาน ViewSets และ Router
การสร้าง REST API โดยไม่ใช้ Framework (Sample_1)
จากไฟล์ตัวอย่าง sample_1/views.py แสดงให้เห็นถึงการใช้ Django เพื่อ Query ข้อมูลจากฐานข้อมูลออกมาแล้ว Return กลับไปยัง client ในรูปแบบของ JSON

class AuthorList ทำหน้าที่รับ HTTP GET จาก client และ Query Author object ทั้งหมดออกมาจากนั้น สร้าง list ของ dictionary ขึ้นมา 1 ตัวชื่อ response เพื่อเก็บข้อมูล id และ name ของ Author จากนั้นจึงใช้คำสั่ง json.dumps (ซึ่งเป็น build in library ของ Python) ในการแปลง list object ให้กลายเป็น JSON Array เพื่อตอบกลับไปยัง client
class AuthorDetail ทำหน้าที่รับ HTTP GET จาก client พร้อมทั้งรับ url parameter 1 ตัวชื่อ ID เพื่อใช้สำหรับดึงข้อมูล Author คนที่ต้องการ ซึ่งมีการเรียกใช้ get_object_or_404 ที่เป็นคำสั่งพิเศษของ Django เพื่อตอบกลับ 404 not found ไปโดยอัตโนมัติ เมื่อผู้ใช้งานใส่ ID ที่ไม่มีอยู่จริงในระบบ
class BookDetail และ BookList ทำหน้าที่เช่นเดียวกันกับของ Author แต่เปลี่ยน object เป็น Book
ตัวอย่างผลการรัน Code เป็นดังต่อไปนี้ตัวอย่างการรัน Class AuthorList ตัวอย่างการรัน Class AuthorDetail
ตัวอย่างการรัน Class AuthorDetail ตัวอย่างการรัน Class BookList
ตัวอย่างการรัน Class BookList ตัวอย่างการรัน Class BookDetail
ตัวอย่างการรัน Class BookDetail




จากตัวอย่างข้างต้นจะเห็นว่าการรอรับ HTTP Request ในทุกๆ method (GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE) และสร้าง JSON Response กลับไปนั้น เป็นเรื่องที่ใช้แรงงานสูงมาก และ code ที่เขียนก็จะซ้ำๆกันเป็นส่วนมาก ดังนั้นจึงเป็นที่มาของการนำ Django Rest framework มาใช้งาน
การติดตั้ง Django Rest framework
ติดตั้งโดยใช้คำสั่ง pip ดังต่อไปนี้

จากนั้นแก้ไขไฟล์ rest_tutorial/settings.py โดยเพิ่ม “rest_framework” เข้าไปใน INSTALLED_APP

Introduction to Serializer (Sample_2)
Serializer คือตัวกลางที่ทำหน้าที่ในการแปลง Django model object ให้กลายเป็น JSON โดยการทำงานของ Serializer จะทำหน้าที่ใน 2 กรณีคือ
การแปลงค่าที่ query ออกมาจากฐานข้อมูลให้กลายเป็น JSON เพื่อเตรียมส่งกลับไปยัง Client (มักจะใช้กับ HTTP GET method) การใช้งานรูปแบบนี้ เราสามารถ new object ของ Serializer ที่ต้องการ แล้วส่ง Django model object เข้าไปเป็น parameter ได้ทันที จากนั้นเมื่อต้องการ JSON สามารถเรียก Serializer.data ได้ เช่น author_serializer = AuthorSerializer(Author.objects.first()) author_json = author_serializer.data
การแปลงค่า JSON ที่รับมาจาก client แล้วแปลงกลับมาเป็น Django object เพื่อเตรียม save ลงฐานข้อมูล (มักใช้กับ HTTP POST, PUT, PATCH method) การใช้งานรูปแบบนี้จะเป็นการสร้าง object ของ serializer โดยการส่ง json ผ่านตัวแปรชื่อ data จากนั้นสามารถเรียกใช้ serializer.is_valid() เพื่อตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของ JSON หรือเรียกใช้ serializer.save() เพื่อบันทึกข้อมูลได้ author_serializer = AuthorSerializer(data=request_json) if author_serializer.is_valid(): author_serializer.save()
จาก Project ตัวอย่างให้ดูในโฟลเดอร์ sample_2ตัวอย่างการประกาศ Serializer โดยใช้ไฟล์ sample_2/serializers.py

การประกาศ Serializer อย่างง่ายที่สุดคือการใช้งาน ModelSerializer โดยมีวิธีการสร้างดังต่อไปนี้
สร้าง class ที่สืบทอด rest_framework.serializers.ModelSerializer
ประกาศ class Meta พร้อมระบุข้อมูลที่จำเป็น 2 อย่างได้แก่ 2.1 model เป็นการระบุ Model Class ที่เราต้องการจะทำ serializ 2.2 fields คือการระบุ field ที่ต้องการ
จากตัวอย่างใน class AuthorSerializer มีการประกาศตัวแปรใหม่ชื่อ book_count ที่จะใช้นับจำนวน Book ทั้งหมดของ Author คนนี้ ( การใช้ reverse relationship ใน Django อ่านเพิ่มเติมได้ ที่นี่ ) ซึ่งจะเห็นว่าสามารถเพิ่ม field ใหม่เข้าไปใน JSON response ได้อย่างง่ายดายการนำ Serializer มาใช้งานใน sample_2/views.py

จากภาพด้านบนเป็นตัวอย่างการนำ Serializer มาใช้งานร่วมกับ View ที่เราได้เคยสร้างไว้ก่อนหน้านี้ จะเห็นว่า code สั้นลงและเป็นระเบียบอย่างชัดเจน
สามารถรัน code ตัวอย่างนี้ได้โดยการเข้าไปที่ URL ดังต่อไปนี้ http://localhost:8000/library/sample_2/author http://localhost:8000/library/sample_2/author/1 http://localhost:8000/library/sample_2/book http://localhost:8000/library/sample_2/book/1
การใช้งาน GenericAPIView (Sample_3)
Django Rest framework สามารถนำมาใช้ใน View เพื่อลดการเขียน code ที่ซ้ำซ้อนออกไปจาก View และ Django Rest framework จะสร้าง GUI สำหรับให้ผู้ใช้งานทดสอบ REST API โดยอัตโนมัติอีกด้วย ซึ่งการนำ Django Rest framework มาใช้งานใน View นี้มีได้หลายวิธีด้วยกัน แต่เพื่อให้กระชับในหัวข้อนี้จะกล่าวถึงการใช้ Generics APIView ซึ่งเมื่อนำมาใช้ร่วมกับ serializer ที่เขียนไว้ก่อนหน้าจะทำให้สร้าง REST API ได้อย่างง่ายมากขึ้น
การใช้งาน Generics APIView ทำได้โดยขั้นตอนดังต่อไปนี้
แก้ไข class ใน view ที่ต้องการให้เปลี่ยนมาสืบทอด generics.XXXView โดย generics ได้แบ่ง API ออกเป็นกลุ่มใหญ่ๆ 2 กลุ่มคือ 1.1 กลุ่มของ API ที่ไม่จำเป็นต้องระบุ ID ของ object ซึ่ง API กลุ่มนี้ได้แก่การทำ GET (เพื่อ list ข้อมูลทั้งหมด) และการทำ POST (เพื่อสร้าง/create object ใหม่ขึ้นในฐานข้อมูล) โดยใช้งานผ่าน generics.ListAPIView, CreateAPIView, ListCreateAPIView 1.2 กลุ่มของ API ที่ต้องระบุ ID ของ object ซึ่ง API กลุ่มนี้ได้แก่การทำ GET (กรณีต้องการ detail ของ object เพียงตัวเดียว), PUT, PATCH, DELETE โดยจะใช้งานผ่าน generics.RetrieveAPIView (GET), UpdateAPIView (PUT), DestroyAPIView (Delete)
ประกาศตัวแปรชื่อ queryset ซึ่งจะเป็นวิธีการระบุถึง Object ที่เราจะใช้ในการ query ออกมา ซึ่งโดยปกติจะใช้ Model.objects.all() แต่อาจมีบางกรณีที่ต้องการ filter object โดยเฉพาะ เช่น Model.objects.filter(is_active=True) เป็นต้น
ประกาศตัวแปรชื่อ serializer_class ซึ่งเป็น Class Serializer ตัวเดียวกับที่ประกาศไว้ก่อนหน้า เพื่อบอกว่า View นี้จะใช้ Serializer ใดในการแปลง Django Model Object ไปอยู่ในรูปแบบของ JSON
เพิ่มเติมกรณีเลือกใช้ GenericsAPI ในกลุ่มที่ต้องระบุ ID จะต้องเพิ่ม ตัวแปรชื่อ lookup_field และระบุ String ของชื่อ field ที่ต้องการนำ URL Parameter ไปค้นหาโดยชื่อของ lookup_field นี้ต้องเป็นชื่อที่ตรงกันทั้งชื่อของ model field และ url parameter field (หากไม่ระบุ lookup_field ต้องกำหนดชื่อตัวแปร URL Parameter ใน urls.py ให้เป็นชื่อ “pk” ซึ่งจะ map กับ id ของ object เท่านั้น)
จาก Project ตัวอย่างดูในโฟลเดอร์ sample_3ตัวอย่าง urls ของไฟล์ sample_3/urls.pyตัวอย่างการนำ Generics APIView มาใช้งานใน sample_3/views.py


จากรูปตัวอย่างจะเห็นว่ามีการแก้ไข code ให้สั้นลง และ code ดังกล่าวยังครอบคลุม REST API ในเกือบทุก Method อีกด้วย
AuthorList ใช้ในการแสดง author ทั้งหมดออกมา โดยสืบทอด generics.ListCreateAPIView เพื่อให้รองรับ GET และ POST API
AuthorDetail ใช้ในการแสดงรายละเอียดของ author ที่ต้องการออกมา โดยหากดูใน urls.py จะเห็นว่ามีการใช้ URL Parameter ชื่อ id และประกาศ lookup_field เป็น id
BookDetail มีการเรียกใช้ method ชื่อ get_queryset() แทนการประกาศตัวแปร queryset ธรรมดา กรณีนี้จะถูกใช้เมื่อมี logic ในการ query object ที่ต้องการที่ค่อนข้างซับซ้อน และในไฟล์ urls.py ได้มีการระบุค่า URL Parameter เป็น “pk” ซึ่งเป็นค่า default ของ Django Rest framework จึงไม่จำเป็นต้องระบุ lookup_field ใน class นี้
สามารถรัน code ตัวอย่างนี้ได้โดยการเข้าไปที่ URL ดังต่อไปนี้ http://localhost:8000/library/sample_3/author http://localhost:8000/library/sample_3/author/1 http://localhost:8000/library/sample_3/book http://localhost:8000/library/sample_3/book/1ตัวอย่างการเรียกใช้งาน URL sample_3/author

การใช้งาน Viewsets และ Router (Sample_4)
Django Rest framework ยังอำนวยความสะดวกให้กับการสร้าง Rest API กรณีที่ API สะท้อนถึงข้อมูลในฐานข้อมูลตรง ๆ โดยผ่านการใช้งาน Viewsets
Viewsets ที่นำมาใช้งานในบทความนี้จะประกอบไปด้วย ModelViewSet คือ การระบุว่า Model ที่ระบุถึงนี้สามารถใช้งานได้ทั้ง GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE ส่วน ReadOnlyModelViewSet คือการระบุว่า Model นี้สามารถใช้งานได้ผ่านทาง GET สำหรับ list และ detail เท่านั้น
Router ถูกนำมาใช้ใน urls.py เพื่อช่วยลด code ที่ต้องเขียนซ้ำๆในการประกาศ URL ไปยัง View ต่าง ๆการประกาศ URL โดยใช้ router ของ sample_4/urls.pyการนำ Viewsets มาใช้ใน sample_4/views.py


สามารถรัน code ตัวอย่างนี้ได้โดยการเข้าไปที่ URL ดังต่อไปนี้ http://localhost:8000/library/sample_4/author http://localhost:8000/library/sample_4/author/1 http://localhost:8000/library/sample_4/book http://localhost:8000/library/sample_4/book/1
REST API Documentation
Django Rest framework ยังช่วยทำ Document ให้โดยอัตโนมัติอีกด้วย โดยวิธีการคือแก้ไขไฟล์ rest_tutorial/urls.py โดยเพิ่ม URL ของ rest_framework.documentation.include_docs_urls ลงไป
และเพิ่มบรรทัดในไฟล์ settings.py ให้ถูกต้องตามรูปต่อไปนี้rest_tutorial/urls.pysettings.py
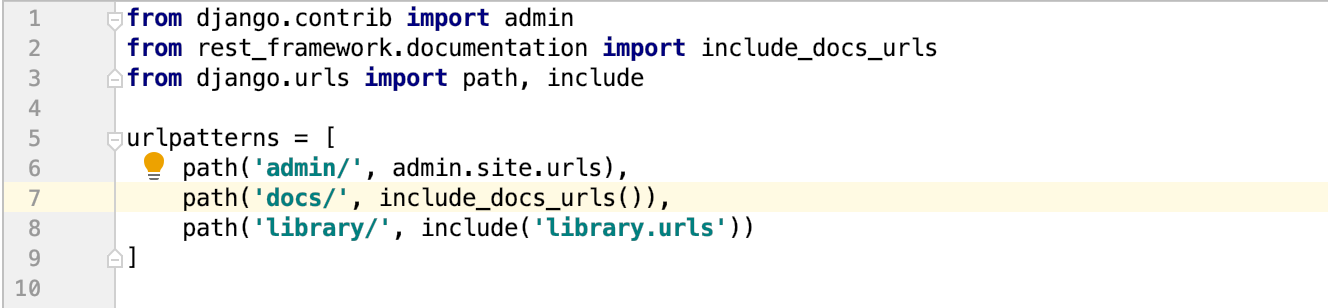

จากนั้นสามารถเข้าดู document ได้ที่ URL
http://localhost:8000/docs/ตัวอย่างหน้าจอ Document ที่ Generate ออกมา

นอกจากนี้ Django Rest framework ยังสามารถสร้าง document ใน format อื่น ๆ ได้ผ่านทาง third party library ต่าง ๆ รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมอ่านได้ ที่นี่
ส่งท้าย
Django Rest framework เป็น framework ที่มีขนาดใหญ่และมีรายละเอียดเยอะมาก ตัวอย่างที่ยกมาอธิบายในบทความนี้เป็นเพียงแค่ส่วนหนึ่งในการเรียกใช้งาน เพื่อให้เห็นภาพรวมของการนำ Django Rest framework มาใช้งาน รายละเอียดทั้งหมดสามารถอ่านต่อได้ ที่นี่ ครับ
212
Last updated