Fundamentals for Data Science
14 JULY 2020

Beginners in the field of data science who are not familiar with programming often have a hard time figuring out where they should start.
With hundreds of questions about how to get started with Python for DS on various forums, this post (and video series) is my attempt to settle all those questions.
I'm a Python evangelist that started off as a Full Stack Python Developer before moving on to data engineering and then data science. My prior experience with Python and a decent grasp of math helped make the switch to data science more comfortable for me.
So, here are the fundamentals to help you with programming in Python.
Before deep dive into the essentials, make sure that you have set up the Python environment and know how to use Jupyter Notebooks(optional).
The basic Python curriculum can be broken down into 4 essential topics that include:
Data types (int, float, strings)
Compound data structures(lists, tuples, and dictionaries)
Conditionals, loops, and functions
Object-oriented programming and using external libraries
Let's briefly go over each one and see what are the fundamentals you should learn.
1. Data Types and Structures
The very first step is to understand how Python interprets a variety of data.
Starting with widely used data types, you should be familiar with integers (int), floats (float), strings (str), and booleans (bool). Here's what you should practice.
Type, typecasting, and I/O functions:
Learning the type of data using the
type()method.
Storing values into variables and input-output functions (
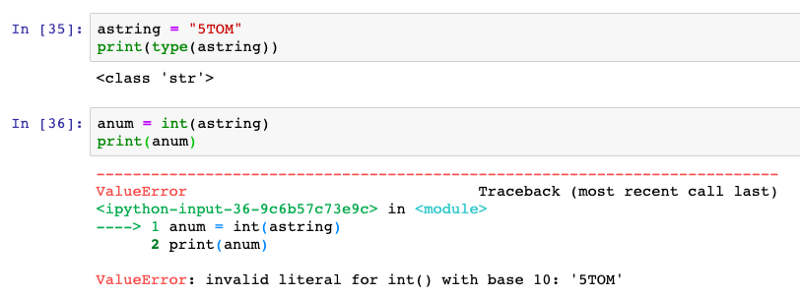
a = 5.67)Typecasting — converting a particular type of variable/data into another type if possible. For example, converting a string of integers into an integer.
But if you'll try to convert an alphanumeric or alphabet string into an integer, it would throw an error:
Once you are familiar with the basic data types and their usage, learn about arithmetic operators and expression evaluations (DMAS) and how you can store the result in a variable for further use.
Strings:
Knowing how to deal with textual data and their operators comes in handy when dealing with the string data type. Practice these concepts:
Concatenating strings using
+Splitting and joining the string using the
split()andjoin()methodChanging the case of the string using
lower()andupper()methodsWorking with substrings of a string
Here’s the Notebook that covers all the points discussed.
2. Compound data structures (lists, tuples, and dictionaries)
Lists and tuples (compound data types):
One of the most commonly used and important data structures in Python are lists. A list is a collection of elements, and the collection can be of the same or varied data types. Understanding lists will eventually pave the way for computing algebraic equations and statistical models on your array of data.
Here are the concepts you should be familiar with:
How multiple data types can be stored in a Python list.
Indexing and slicing to access a specific element or sub-list of the list.
Helper methods for sorting, reversing, deleting elements, copying, and appending.
Nested lists — lists containing lists. For example,
[1,2,3, [10,11]].Addition in a list.
Multiplying the list with a scalar:

Tuples are an immutable ordered sequence of items. They are similar to lists, but the key difference is that tuples are immutable whereas lists are mutable.
Concepts to focus on:
Indexing and slicing (similar to lists).
Nested tuples.
Adding tuples and helper methods like
count()andindex().
Dictionaries
These are another type of collection in Python. While lists are integer indexed, dictionaries are more like addresses. Dictionaries have key-value pairs, and keys are analogous to indexes in lists.

To access an element, you need to pass the key in squared brackets.

Concepts to focus on:
Iterating through a dictionary (also covered in loops).
Using helper methods like
get(),pop(),items(),keys(),update(), and so on.
Notebook for the above topics can be found here.
3. Conditionals, Loops, and Functions
Conditions and Branching
Python uses these boolean variables to assess conditions. Whenever there is a comparison or evaluation, boolean values are the resulting solution.
The comparison in the image needs to be observed carefully as people confuse the assignment operator (=) with the comparison operator (==).
Boolean operators (or, and, not)
These are used to evaluate complex assertions together.
or— One of the many comparisons should be true for the entire condition to be true.and— All of the comparisons should be true for the entire condition to be true.not— Checks for the opposite of the comparison specified.

Concepts to learn:
if,else, andelifstatements to construct your condition.Making complex comparisons in one condition.
Keeping indentation in mind while writing nested
if/elsestatements.Using boolean,
in,is, andnotoperators.
Loops
Often you'll need to do a repetitive task, and loops will be your best friend to eliminate the overhead of code redundancy. You’ll often need to iterate through each element of a list or dictionary, and loops come in handy for that. while and for are two types of loops.
Focus on:
The
range()function and iterating through a sequence usingforloops.whileloops
Iterating through lists and appending (or any other task with list items) elements in a particular order
Using
break,pass, andcontinuekeywords.
List Comprehension
A sophisticated and succinct way of creating a list using and iterable followed by a for clause.
For example, you can create a list of 9 cubes as shown in the example above using list comprehension.
Functions
While working on a big project, maintaining code becomes a real chore. If your code performs similar tasks many times, a convenient way to manage your code is by using functions.
A function is a block of code that performs some operations on input data and gives you the desired output.
Using functions makes the code more readable, reduces redundancy, makes the code reusable, and saves time.
Python uses indentation to create blocks of code. This is an example of a function:
We define a function using the def keyword followed by the name of the function and arguments (input) within the parentheses, followed by a colon.
The body of the function is the indented code block, and the output is returned with the return keyword.
You call a function by specifying the name and passing the arguments within the parentheses as per the definition.

More examples and details here.
4. Object-Oriented programming and using external libraries
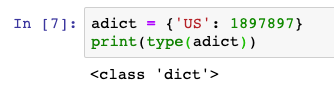
We have been using the helper methods for lists, dictionaries, and other data types, but where are these coming from?
When we say list or dict, we are actually interacting with a list class object or a dict class object. Printing the type of a dictionary object will show you that it is a class dict object.
These are all pre-defined classes in the Python language, and they make our tasks very easy and convenient.
Objects are instance of a class and are defined as an encapsulation of variables (data) and functions into a single entity. They have access to the variables (attributes) and methods (functions) from classes.
Now the question is, can we create our own custom classes and objects? The answer is YES.
Here is how you define a class and an object of it:
You can then access the attributes and methods using the dot(.) operator.

Using External Libraries/Modules
One of the main reasons to use Python for data science is the amazing community that develops high-quality packages for different domains and problems. Using external libraries and modules is an integral part of working on projects in Python.
These libraries and modules have defined classes, attributes, and methods that we can use to accomplish our tasks. For example, the math library contains many mathematical functions that we can use to carry out our calculations. The libraries are .py files.
You should learn to:
Import libraries in your workspace

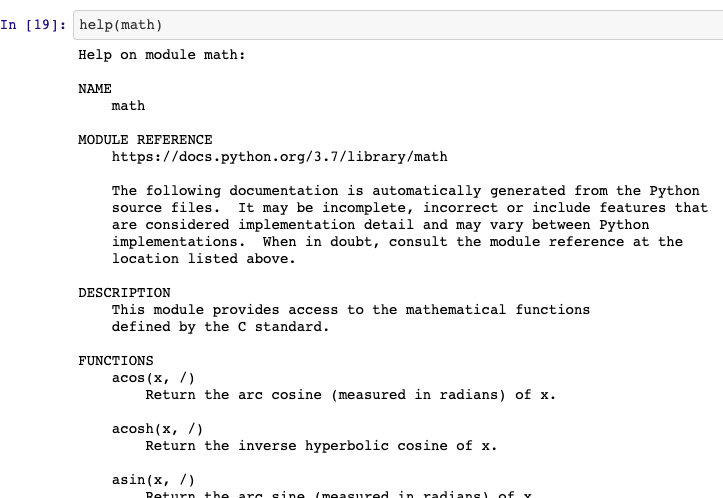
Using the
helpfunction to learn about a library or function
Importing the required function directly.

How to read the documentation of the well-known packages like pandas, numpy, and sklearn and use them in your projects
That should cover the fundamentals of Python and get you started with data science.
There are a few other features, functionalities, and data types that you’ll become familiar with over time as you work on more and more projects.
You can go through these concepts in GitHub repo where you’ll find the exercise notebooks as well:
Reference : https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-fundamentals-for-data-science/
Last updated