Handle Timezones
7 APRIL 2020
How to Handle Timezones and Synchronize Your Software with International Customers

When you develop some software you may not think about timezones at first. Unless you live in a country which has to deal with multiple time zones, such as the United States or Russia.
I recently came across an issue involving timezones. There were some unit tests making assertions about dates that used to work at my office in France but weren't working in Morocco for new members on our team.Here is the unit test working in France but not in Morocco

This was an opportunity for me to learn how to correctly handle dates and times for international software. In this article, I’ll introduce time zone issues and share some rules to follow.
Quick introduction to time zones
As the earth is kind of a sphere, the sun is rising in Japan while it's setting in America. If everyone used global time, let’s say 09:00 would be sunrise in Japan, but for Americans it would be sunset. Not very handy.
To make sure the time is coordinated with the sun for everyone, it’s necessary to shift from global time according to your location. As a result, the globe gets split into time zones and each gets an offset. This offset is a number of minutes to add to the global time to get your time zone time. It can be either positive or negative.Standard world time zones — Illustration by Hellerick from Wikimedia Commons

Global time is called UTC, it stands for Coordinated Universal Time. You may also heard about GMT which is a time zone without any offset.
For instance, when it’s 10:50 at UTC, it’s also 03:50 in San Francisco with a -0700 offset and 18:50 in Beijing with a +0800 offset. Yet, the shift isn’t only in whole hours: Nepal's offset is +0545. You can check it out on Wikipedia.
In addition of this offset, which comes with the time zone, some countries also shift clocks twice a year. DST or summer time adds one hour to the time zone offset before summer. Then, the clock is reset to the time zone time in winter. The goal is to make the daytime longer.
The most common way to figure out a time zone is by using the IANA Time Zone Database. You end up with a string such as Europe/Paris following the Area/City pattern. Besides, Microsoft maintains its own Microsoft Time Zone Database used on its operating systems. But this can cause issues when running cross-platform .NET Core apps.
IANA is still the go-to. The Microsoft database isn't updated often, it contains less history, fairly curious time zone names (eg: Romantic Standard Time) and is error prone. For example, try to not mix up Arab , Arabic and Arabian Standard Time. For more details on each database and their differences, check out this article.
One last thing: there are plenty of ways to write a date. Fortunately, the ISO 8601 specification sets a common rule for date formatting.
How computers handle dates
Computers are only able to perform operations using numbers. This means that 2020-08-01 +1 is not equal to 2020-08-02 and can’t be handled.
In order to work with dates more easily, we can represent dates as numbers. This is what timestamps are all about. It’s the number of milliseconds elapsed from a pre-defined date (or epoch) to the specified date.
Great, let’s choose an epoch then! Actually, the common epoch has already been set and its value is January 1, 1970 (midnight UTC).

To make sure you understood, run the previous snippet in your browser. What? You didn’t get the same result?
Ok, I cheated a bit to get this result… I should get Thu Jan 01 1970 01:00 GMT+0100 because my computer time zone is set to Europe/Paris.
Actually, this moment with a zero timestamp is midnight in Greenwich, but also 05:45 in Mumbai and even 1969-12-31T16:30 in San Francisco when you consider their time zone’s offset.
Rule #1 : Timestamps are only for saving, not for displaying. It's considered on UTC because it doesn’t include any offset or time zone.
You didn’t get the “right” date before because JavaScript uses your local time zone to show the most accurate date/time to you.
Now, try the following snippet. I’m sure you’ll get the same result as I did:

Yes, the zero timestamp is 1970-01-01T00:00:00 at UTC for everyone around the globe. Still, it’s not true if you choose another time zone.
To sum up, toString shows the date using your local time zone while toUTCString is based on UTC. Also don’t be fooled by toISOString which is the same as toUTCString but outputs the ISO 8601 format (its name should be toUTCISOString).
I recommend the date command to convert a second timestamp (not milliseconds) into a readable string. Using this command with the UTC option makes sure it doesn't take your computer/browser's time zone into account.
Let’s fix our unit test
The problem I encountered with time zones was in my unit tests. Take the time to read it and understand what it’s supposed to assert:

In this test, the goal is to check that setHours sets the date’s hours and minutes to zero (midnight). I first choose a random timestamp which isn’t at midnight. Then compare the result with the timestamp for the same day at midnight.
Actually it’s working – but only if your time zone offset is +0200 (including DST) at this moment. For instance, it’s not working for Africa/Casablanca ( +0100 including DST). Let’s see how those timestamps are printed:
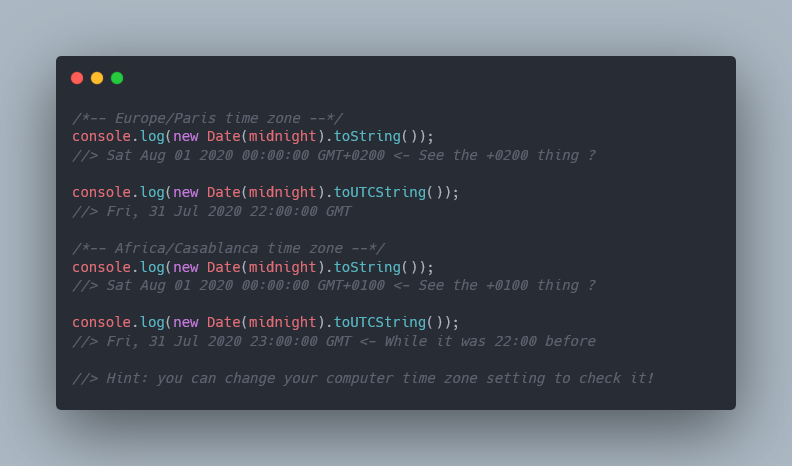
That’s it, the UTC date for both results isn't the same. It also means the resulting timestamps aren’t the same either.
As you can see, the offset for Paris is +0200 and +0100 for Casablanca. But both display midnight with toString. This means that the setHours function uses your computer time zone to perform the operation. And toString displays the date using your time zone.
This is not the only issue with this test: what if you run this test in San Fransisco? Right, the day would be 2020-07-31 for both dates because of the -0700 offset.
The safest way to make this test reliable and work all around the world is to use a date in your local time zone. You’ll not use timestamps to set initial dates anymore.

We can enhance the previous rule about timestamps:
Rule #2 : String dates are suitable for display using the user's time zone and computations. They aren’t on UTC but generally include an offset.
Keep it on date on the server side
The rule about timestamps still applies on the server side. However the second rule about using string dates can’t be used.
Indeed, in some case with technologies such as PHP, Java, and Rails the pages are rendered on server side (SSR). This means all the HTML is generated by the server and it has no idea about the client's time zone. Think about the server – it’s nothing more than a computer on the globe. It also has its own time zone but it’s not necessarily the same as the client's time zone.
Rule #3 : Servers might either know the client's time zone or send a date on UTC. The server's time zone doesn’t matter.
The new Java 8 Date/Time is considered one of the most understandable and clear APIs that helps you deal with date. I’m not going to explain how it works here but let’s review some interesting points.
LocalDateTime, OffsetDateTime and ZonedDateTime are the 3 classes provided to compute and display date and time. No more Date or DateTime which mix up displaying the local date and UTC date.
The following examples are extracted from this awesome article (written by Jonas Konrad) which describes the Java 8 Date/Time API with a bunch of examples. By the way, many thanks to him, he kindly let me quote its pieces of code!
Let’s look at the differences between the 3 classes:

There is a small but important difference between OffsetDateTime and ZonedDateTime, did you notice it?
As its name says, OffsetDateTime is only aware of an offset between the local date and UTC. This means that it handles DST differently from a date which is attached to a time zone.

The example with a time zone seems to be the right behavior. Actually, both are correct because adding 1 day can either mean:
Add 1 day and keep the same hour (handles DST with
ZonedDateTime)Add 24 hours to the current date (with
OffsetDateTime).
Remember Rule #1 about timestamps? You should only use a UTC timestamp for saving. The Java API provides an Instant class which is a timestamp you can get from any of the three classes used for displaying the date.

Final thoughts
In this article, you've learned that timestamps are for saving (Rule #1) and string dates are for displaying (Rule #2). Did you notice that the number of seconds from the epoch is quite a big number?
That’s why after the Unix Millennium Bug (Y2K) problem comes the Y2K38 problem which stands for the year 2038. At 2038-01-19T03:14:07Z the timestamp (in seconds) will reach its maximum for 32-bit signed integers 2,147,483,647 . It will then turn into a negative number after adding one more second.This sign indicates January 1900 instead of January 2000 — Picture from Wikipedia Commons

On forums, people say they don’t care because their software won't be used for 20 years without re-writing. Well, that might be true but let’s still think about some solutions (with MySQL):
Update
TIMESTAMPtype to 64-bit signed integersSave UTC dates in
DATETIMEcolumns instead ofTIMESTAMP
Both solutions have their advantages and drawbacks. The first one seems like a hack which reports the issue later. Yet, it fixes the issue for a very, very long time. Your software will be deprecated and not used anymore when the problem occurs again.
The second solution works for an almost infinite amount of time (up to 9999-12-31T23:59:59Z).
Using TIMESTAMP is recommended for logs, while DATETIME is better for other needs. Remember a timestamp can’t store a date prior to 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z and not after 2038-01-19T03:14:07Z. This means you should use DATETIME to save dates far in the past and future.
Besides, in MySQL TIMESTAMPs are stored at UTC but displayed according to a specified time zone (and converted to UTC before saving). This mechanism comes in handy when you need to get a local date and doesn’t exist with DATETIME.
A last word about moment.js, a popular library to deal with dates. I first experimented an issue and wanted to warn you about it:

Both console.logs will output 2020-08-02 00:00. If you’re used to functional programming, you expect hours and minutes to return a new moment object because they are pure functions. It’s not the case – they modify the input date and return it for easy chaining.
Thanks for reading up to the end. I hope this experience of mine has been useful to you. By the way, I’m not very confident about the choice between TIMESTAMP and DATETIME, so don’t hesitate to share your experience!
If you found this article useful, please share it on social media to help others find it and to show your support! 👊
Don’t forget to check my author page for upcoming articles 🙏
Reference : https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/synchronize-your-software-with-international-customers/
Last updated